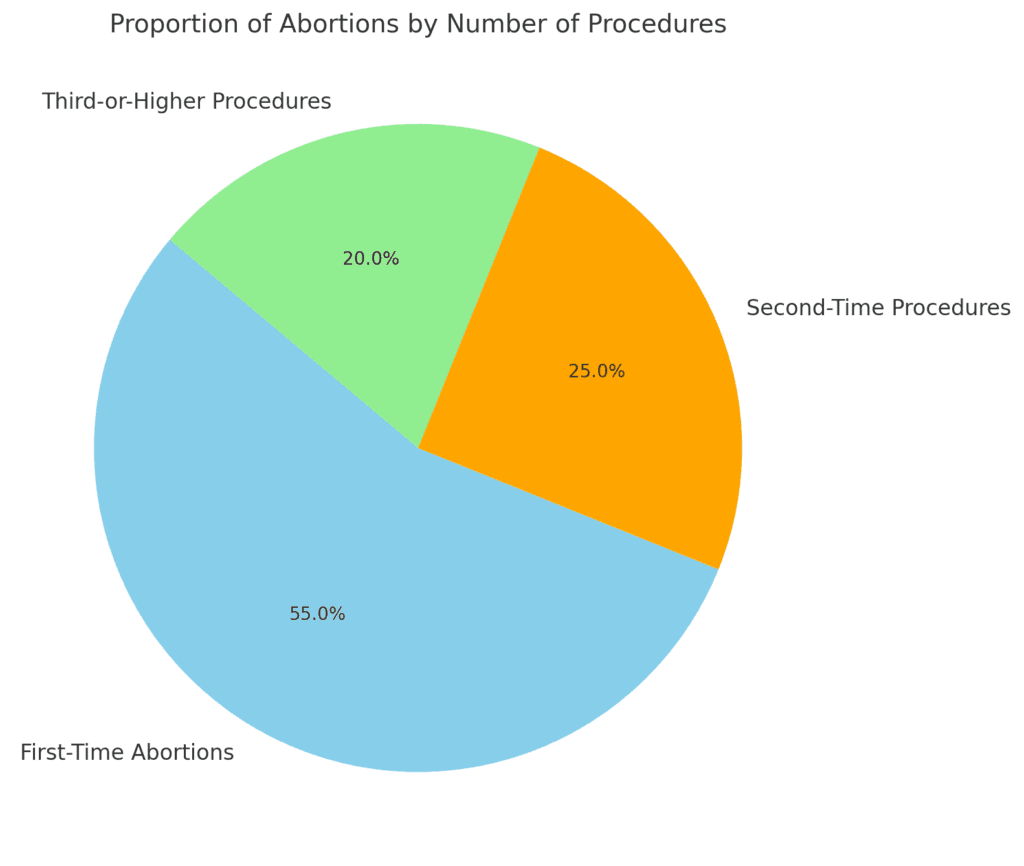
"This pie chart illustrates the distribution of abortions by the number of procedures, highlighting the proportion of first-time, second-time, and third-or-higher procedures."
Abortion remains one of the most debated issues globally, touching on moral, personal, and political dimensions. However, examining abortion statistics can provide valuable insights into the procedure’s prevalence, the reasons behind it, and the frequency of repeat procedures. These numbers not only reflect individual decisions but also reveal societal norms, economic pressures, and cultural attitudes toward life and choice.
In this article, we explore abortion statistics and repeat procedures, breaking down what the numbers mean for women, families, and society.
1. Global and U.S. Abortion Rates
Global Abortion Rates
Abortion is a global phenomenon. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 73 million abortions occur worldwide each year. This accounts for nearly 29% of all pregnancies, showcasing the significant role abortion plays in global reproductive health. These rates highlight disparities in access to contraception and family planning resources across different regions.
U.S. Abortion Rates
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recorded around 620,000 abortions in 2020, a significant decline from earlier decades. This equates to a rate of 11.4 abortions per 1,000 women of reproductive age (15-44). The downward trend reflects advancements in contraceptive use, education, and access to healthcare. However, regional differences persist, influenced by state policies and healthcare access.
2. Reasons for Seeking Abortions
Economic Pressures
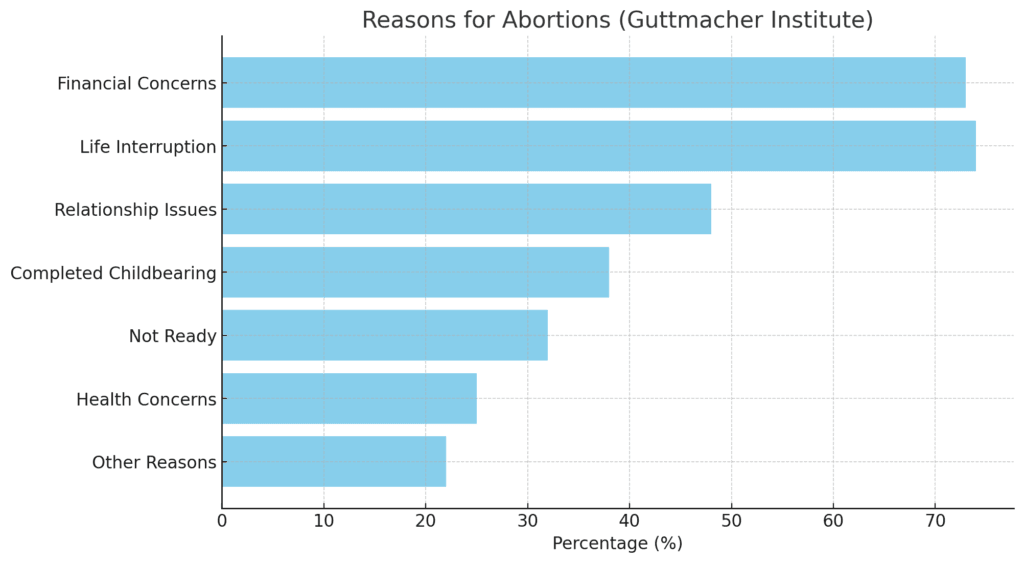
Financial instability is the leading reason women seek abortions. A Guttmacher Institute study found that 73% of women cited economic hardship as a key factor. This statistic underscores the significant role that poverty and limited access to resources play in reproductive decisions.
Timing and Personal Readiness
Around 48% of women who have abortions report that they are not ready to become parents. Factors such as pursuing education, career goals, or personal stability heavily influence these decisions, revealing how societal and individual priorities intersect.
Relationship and Support Issues
For 31% of women, the lack of support from a partner or relationship instability is a significant motivator. This reflects broader challenges related to family dynamics, social support systems, and cultural norms.
Health Concerns
Health risks to the mother or fetus account for approximately 12% of abortions. These include severe fetal abnormalities or conditions that jeopardize the mother’s health, underscoring the complex medical considerations behind some abortion decisions.
3. Repeat Procedures: Frequency and Causes
Prevalence of Repeat Abortions
Repeat abortions are a critical aspect of the broader conversation. In the United States, nearly 45% of abortions are performed on women who have had at least one prior abortion. Of these, around 20% involve a third procedure, and a smaller percentage involves four or more.
Contraception Access and Usage
One of the driving factors behind repeat abortions is inconsistent access to contraception. Women facing financial barriers, healthcare disparities, or inadequate sex education often struggle to maintain effective contraceptive use. This highlights the importance of accessible and affordable reproductive healthcare.
Social Implications
The prevalence of repeat abortions reflects systemic challenges, including poverty, gaps in sex education, and inadequate healthcare systems. Addressing these issues can help reduce unintended pregnancies and provide better reproductive outcomes.

4. Timing of Abortions: When They Occur
First Trimester Abortions
The majority of abortions—about 92%—occur during the first 13 weeks of pregnancy. Early access to care and advancements in medication abortions have made it easier for women to terminate pregnancies earlier.
Second Trimester Abortions
Around 7% of abortions occur between 14 and 20 weeks. Reasons for second-trimester procedures include delayed confirmation of pregnancy, financial or logistical barriers to accessing care, or the discovery of health complications.
Third Trimester Abortions
Abortions performed after 21 weeks are extremely rare, making up less than 1% of all cases. These are often due to severe fetal abnormalities or significant health risks to the mother, situations that demand complex medical and ethical considerations.
5. Demographic Insights: Age, Race, and Socioeconomic Status
Age
Women in their 20s account for the majority of abortions, with about 57% occurring among women aged 20-29. Teenagers represent around 9%, while women over 30 make up approximately 34% of all abortions. These statistics reflect life stage differences in reproductive choices and priorities.
Race and Ethnicity
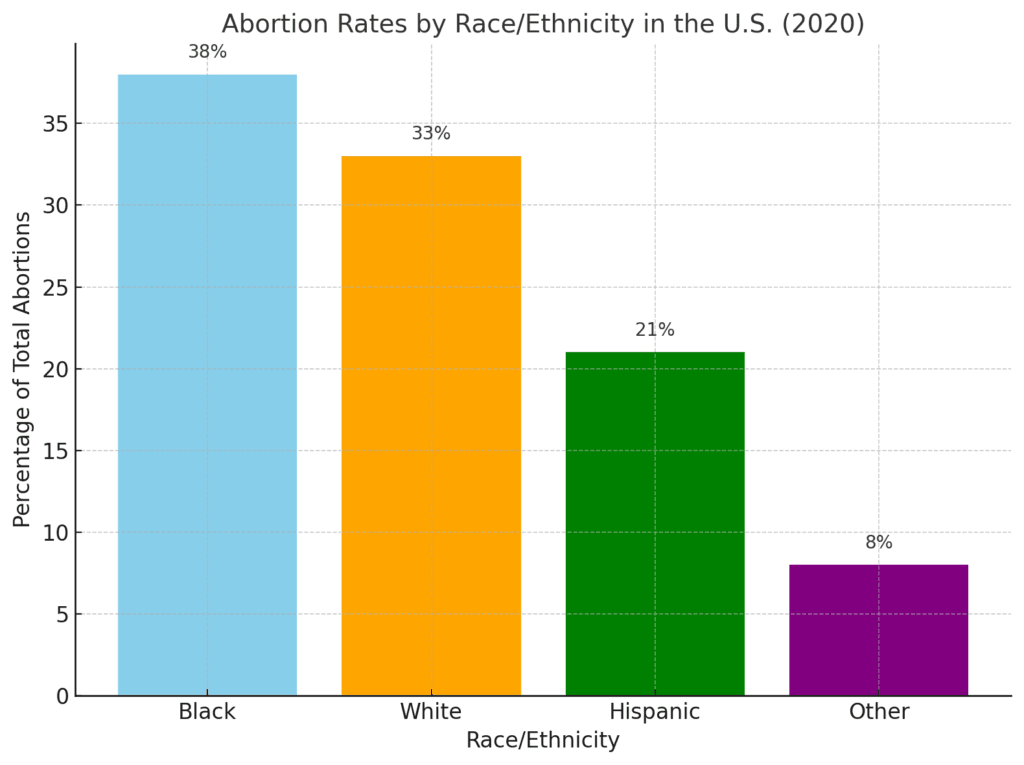
Racial disparities are evident in abortion rates. For instance, Black women accounted for 38% of abortions in the U.S. in 2020, despite comprising a smaller proportion of the population. These disparities highlight systemic issues like unequal access to healthcare, economic inequality, and educational gaps.
Economic Status
Low-income women are disproportionately represented in abortion statistics. Financial barriers to contraception, healthcare, and childcare drive many decisions, underscoring the intersection of poverty and reproductive health.
6. Psychological and Social Impacts of Abortion
Mental Health Outcomes
The psychological impact of abortion varies. While some women report feelings of guilt or sadness, particularly if influenced by external pressures, others experience relief. Studies suggest that supportive environments and counseling can mitigate negative mental health outcomes.
Social Stigma
Stigma surrounding abortion remains pervasive, often leading to isolation and emotional distress. Addressing this stigma through education and compassionate care can create a more supportive environment for women facing difficult choices.
7. Implications for Society and Policy
Addressing Root Causes
Abortion statistics and repeat procedures reveal a need for systemic solutions. Policies that enhance access to contraception, improve sex education, and address economic inequality can help reduce unintended pregnancies and support women in making informed decisions.
Supporting Life-Affirming Choices
Creating environments where women feel supported to carry pregnancies to term is essential. Initiatives such as paid parental leave, affordable childcare, and housing assistance can make parenting more viable and desirable, reducing the perceived need for abortion.
Conclusion: What Abortion Statistics Tell Us
Abortion statistics and repeat procedures illuminate the complex interplay of societal, economic, and personal factors driving reproductive choices. They highlight not only the challenges women face but also the areas where society can provide better support.
From improving access to contraception to addressing economic barriers, a holistic approach to reproductive health can empower women and promote life-affirming solutions. By understanding these numbers, we can begin to address the root causes of abortion and create a society that values both individual choice and human dignity.

Further Reading on Paranoid Prophet
- Paranoid Prophet – The Fetal Tissue Black Market Controversy
Investigates the ethical and spiritual implications of the black market trade in fetal tissue, drawing attention to the commodification of human life.
Read more here - Paranoid Prophet – The Language of Abortion: A Biblical Perspective
Explores how the language surrounding abortion shapes societal understanding and contrasts this with biblical teachings.
Read more here - Paranoid Prophet – Biblical Perspective on Abortion: Eternal Consequences
Discusses the eternal implications of abortion through the lens of scripture, emphasizing the sanctity of life and accountability before God.
Read more here - Paranoid Prophet – Media Coverage of Project 2025 Agenda: Reproductive Rights and Politics
Analyzes how the media portrays the reproductive rights debate within the context of the Project 2025 agenda, highlighting biases and moral perspectives.
Read more here - Paranoid Prophet – Options for Unexpected Pregnancy: A Biblical View
Offers biblically grounded guidance for women facing unplanned pregnancies, focusing on life-affirming alternatives and spiritual support.
Read more here
SOURCES
To enhance the credibility and depth of your article, consider incorporating the following authoritative sources that provide comprehensive data on abortion statistics and repeat procedures:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Abortion Surveillance Reports
The CDC publishes annual surveillance reports detailing the number and characteristics of women obtaining legal induced abortions in the United States. These reports offer insights into trends over time, demographic breakdowns, and procedural details. CDC - Guttmacher Institute – Repeat Abortion in the United States
This report delves into the prevalence and demographics of repeat abortion patients, analyzing factors such as age, socioeconomic status, and contraceptive use. It provides a nuanced understanding of the circumstances leading to multiple abortions. Guttmacher Institute - Pew Research Center – What the Data Says About Abortion in the U.S.
Pew Research Center compiles data from various sources to answer common questions about abortion in America, including statistics on repeat abortions and demographic trends. Pew Research Center - Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) – Key Facts on Abortion in the United States
KFF provides up-to-date statistics on abortion incidence, demographic characteristics of women who have abortions, and state-level data, offering a comprehensive overview of abortion trends in the U.S. Kaiser Family Foundation - Statista – Abortion in the U.S. – Statistics & Facts
Statista aggregates data on abortion rates, demographic breakdowns, and historical trends, presenting the information in accessible charts and graphs. Statista
By integrating data and insights from these sources, your article will provide readers with a well-rounded and evidence-based perspective on abortion statistics and the factors contributing to repeat procedures.
FAQ: Understanding Abortion Statistics, Reasons, and Trends
Biblical Perspective on Abortion
- What does the Bible say about abortion and when life begins?
The Bible emphasizes the sanctity of life and implies that life begins in the womb, referencing verses like Jeremiah 1:5. - How does Christianity address abortion in cases of rape or incest?
While the Bible does not explicitly address these situations, Christian teachings encourage compassion and support for all life. - What does the Bible teach about forgiveness for abortion?
Scripture highlights God’s grace and forgiveness for those who repent, offering hope to individuals who regret their abortion. - How can churches help women facing unplanned pregnancies?
Churches can provide emotional, spiritual, and financial support, encouraging life-affirming choices aligned with biblical principles. - Is abortion considered murder according to biblical teachings?
Many Christians interpret abortion as the taking of innocent life, aligning it with the commandment, “Thou shall not kill.”
Statistics and Adverse Impacts
- How many abortions are performed annually worldwide?
The World Health Organization estimates around 73 million abortions occur globally each year, representing 29% of pregnancies. - What percentage of abortions are repeat procedures?
In the United States, approximately 45% of abortions involve women who have had at least one prior abortion. - What are the psychological effects of abortion on women?
Some studies report increased feelings of guilt, sadness, or depression, while others indicate relief depending on personal circumstances. - How do abortions impact physical health?
While first-trimester abortions are generally safe, later-term procedures can carry risks like infection, excessive bleeding, or uterine damage. - What are the economic factors driving high abortion rates?
Financial instability is a leading cause, with 73% of women citing economic hardship as a primary reason for seeking an abortion. - How does repeat abortion reflect gaps in contraception access?
Women facing economic and healthcare barriers often struggle to maintain consistent contraceptive use, leading to repeat procedures. - What are the societal consequences of high abortion rates?
High abortion rates highlight systemic issues such as poverty, lack of healthcare access, and inadequate family support systems. - What is the role of education in reducing abortion rates?
Comprehensive sex education has been shown to lower unintended pregnancies, which directly impacts abortion rates.
Medical and Ethical Concerns
- What are the health risks of second-trimester abortions?
Second-trimester procedures carry higher risks, including complications like cervical injury and uterine perforation. - Why are late-term abortions controversial?
Late-term abortions, though rare, raise ethical questions due to the viability of the fetus and health risks to the mother. - What is the link between abortion and mental health issues?
Mental health impacts vary, with some women reporting long-term emotional distress, while others feel relief after the procedure. - How does the black market for fetal tissue affect abortion ethics?
The trade in fetal tissue raises serious concerns about the commodification of human life and ethical boundaries in medical research. - How does improved access to contraception reduce abortion rates?
Affordable contraception empowers women to avoid unplanned pregnancies, which is critical to reducing the need for abortion.
Policy and Advocacy
- What policies effectively reduce abortion rates?
Policies like expanded healthcare access, childcare support, and economic assistance for families reduce the demand for abortions. - What role does the Project 2025 agenda play in reproductive rights debates?
The Project 2025 agenda focuses on promoting life-affirming values and addressing root causes of abortion, such as poverty and lack of support. - How can governments support women with unplanned pregnancies?
Governments can offer financial aid, housing, healthcare, and education programs to help women choose life-affirming alternatives. - What is the role of faith-based organizations in reducing abortions?
Faith-based organizations provide counseling, resources, and community support to women in crisis pregnancies.
Media and Social Stigma
- How does media coverage influence public opinion on abortion?
Media narratives often shape public perceptions, framing abortion as a political issue rather than a moral or societal concern. - What are the societal effects of abortion stigma?
Abortion stigma can lead to isolation, mental health struggles, and difficulty accessing supportive resources. - How can society foster compassionate support for women post-abortion?
By reducing stigma and offering emotional and spiritual care, society can help women heal and find peace after an abortion.


